Pulmonary Embolism and COVID-19
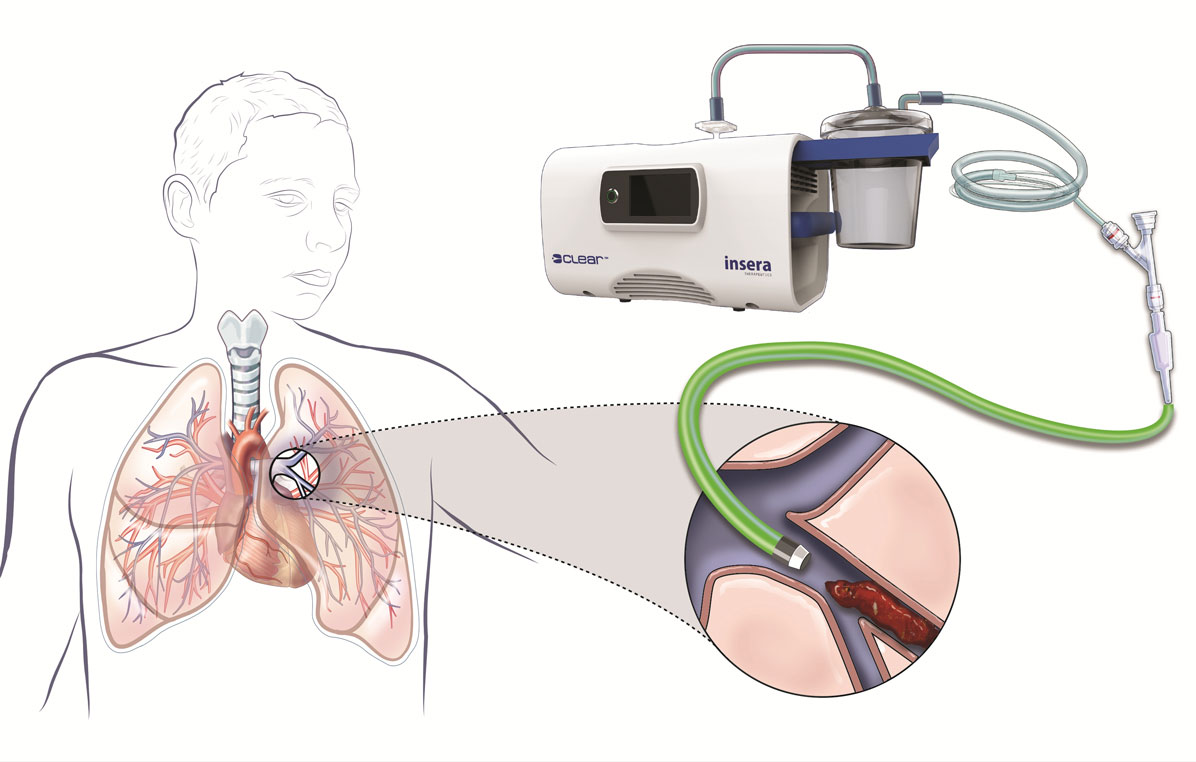
Risk of Pulmonary Embolism after COVID-19 Recovery
Coronavirus is the infectious disease brought about by an as of late found SARS-CoV-2. How we might interpret COVID-19 keeps on developing as the disease stays a worldwide general wellbeing crisis. SARS-CoV-2 pollution is connected with an extended bet of venous thromboembolism (VTE), which is typical during dynamic sickness anyway astounding in milder cases. Covid patients had a higher bet of significant vein circulatory trouble, or DVT, (blood coagulation in the leg) for up to 90 days after disease; pneumonic embolism (blood coagulation in the lung) for up to a half-year; and a depleting event for up to two months.
Plenty of research has been led to examine the disease cycle and the ideal treatment modalities yet there stay numerous questions. Disease with SARS-CoV-2 is frequently asymptomatic yet prompts liberated immune reactions with multi-organ disappointment and critical sickness in a minority of patients.
What is Pulmonary Embolism?
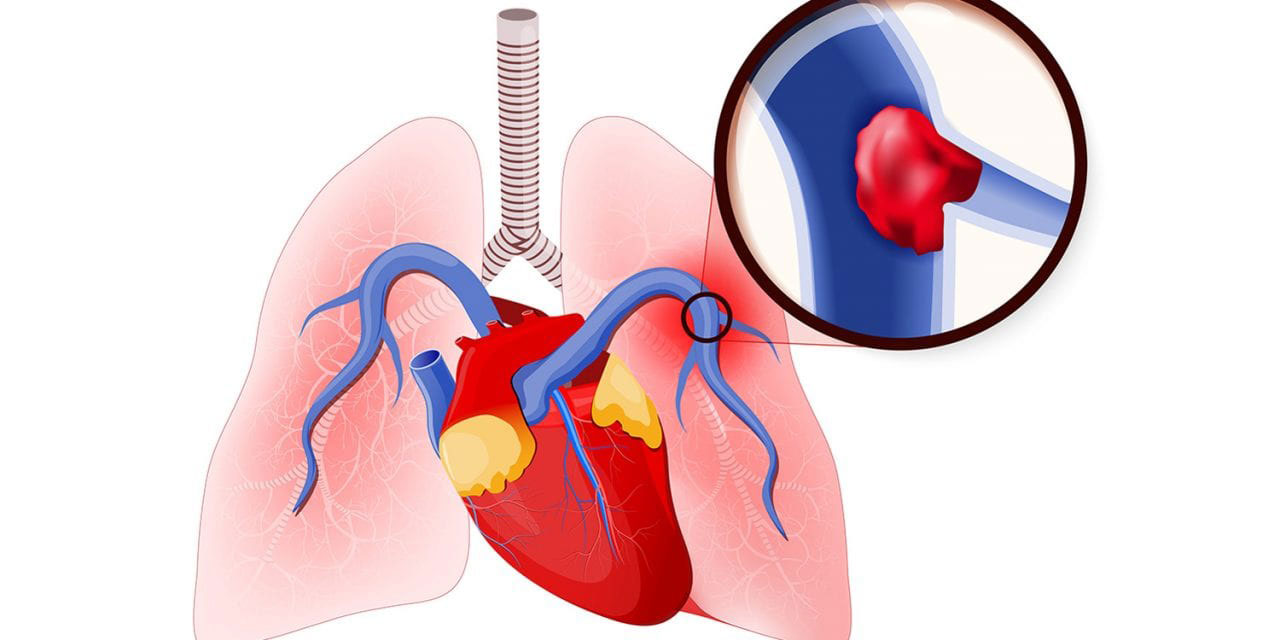
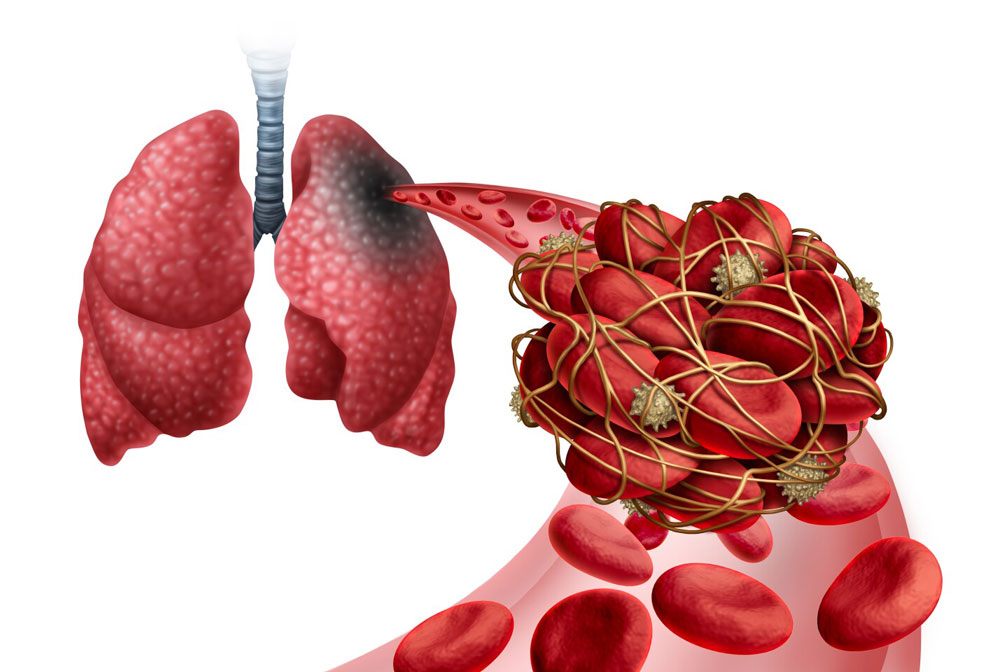
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in your lungs. Much of the time, pulmonary embolism is brought about by blood clots that move to the lungs from deep veins in the legs or, once in a while, from veins in different pieces of the body (deep vein thrombosis).
Since the clots block bloodstream to the lungs, pulmonary embolism can life-undermine. Nonetheless, brief treatment extraordinarily decreases the risk of death. Trying to prevent blood clots in your legs will assist with protection against pulmonary embolism.
If a clot develops in a vein and it stays there, it’s called a thrombus. If the clot detaches from the wall of the vein and travels to another part of your body, it’s called an embolus. If PEs are not treated quickly, they can cause heart or lung damage and even death.
What leads to Pulmonary Embolism?
Blood clots can shape for an assortment of reasons. Pulmonary embolisms (PEs) are most frequently brought about by deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a condition wherein blood clots structure in veins deep in the body. The blood clots that most frequently cause PEs start in the legs or pelvis.
Blood clots in the deep veins of the body can have a few distinct causes, including:
- Injury or damage: Injuries such as bone fractures or muscle tears might result in damage of the blood vessels, resulting in clots.
- Inactivity: During significant stretches of inactivity, gravity makes blood gather in the least region of your body, which might prompt a blood coagulation. This could happen on the off chance that you're sitting for an extended excursion or on the other hand in the event that you're lying in bed recuperating from a disease.
- Medical conditions: Some ailments make blood clump effectively, which can prompt PE. Medicines that include a medical procedure frequently lead to transient bed rest or restricted development, which can make coagulating more probable. Additionally, certain clinical treatments for disease can have secondary effects like thickening in the blood. This jeopardizes you for DVT and PE.
There are extra risk factors that increment your chances of having the kind of blood clump that can cause PE.
A pulmonary embolism might break down all alone; it is only occasionally deadly when analyzed and treated appropriately. Be that as it may, whenever left untreated, it tends to be significant, prompting other unexpected problems, including demise. A pulmonary embolism can:
- Cause damage to the heart.
- Be risky, depending upon the size of the coagulation.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism?
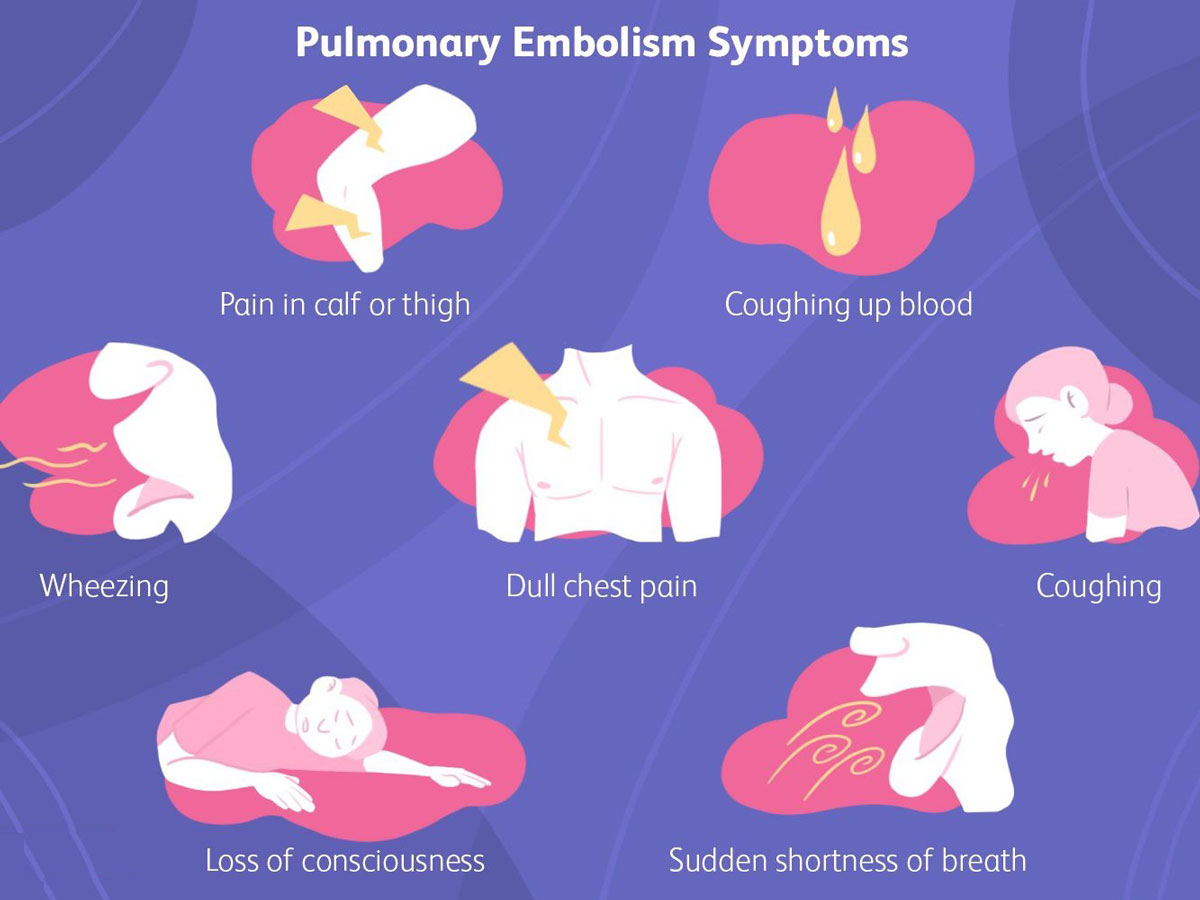
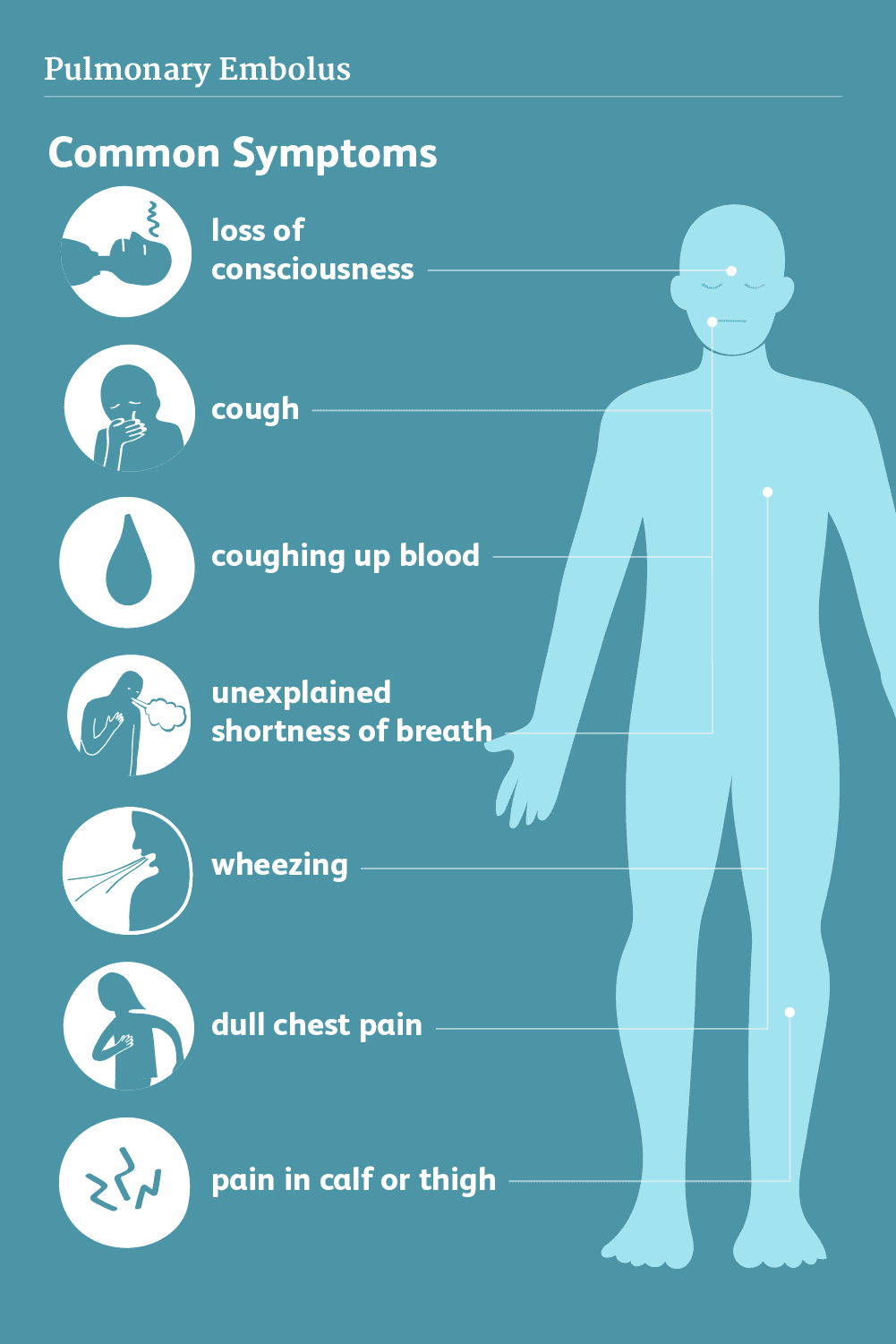
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism differ, contingent upon the seriousness of the coagulation. Albeit the vast majority with a pulmonary embolism experience symptoms, some will not. The principal signs are typically windedness and chest pains that deteriorate assuming you strive. You might hack up horrendous sputum. In the event that you have these symptoms stand out enough to be noticed immediately. Pulmonary embolism is serious however entirely treatable. Fast treatment enormously decreases the opportunity of death.
Symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath suddenly – in case you’ve been active or at rest.
- Sharp pain in your chest, arm, shoulder, neck or jaw that is unexplained.
- Pain similar to symptoms of a heart attack.
- Cough accompanied with or without blood in sputum (mucus).
- Pale, clammy or bluish-colored skin.
- Rapid heartbeat (pulse).
- Excessive sweating.
- Sometimes feeling anxious, light-headed, fainting or passing out.
- Wheezing.
Post-COVID Pulmonary Embolism?
COVID-19 increases people's risk of dangerous blood clots and bleeding for months after infection. Even patients with mild COVID-19 had an increased risk of DVT and pulmonary embolism, the study found. While no increased risk of bleeding was found in those with mild COVID, there was a noticeable increase in patients with more severe infection.
Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
Even patients with mild COVID-19 had an increased risk of DVT and pulmonary embolism, the study found. While no increased risk of bleeding was found in those with mild COVID, there was a noticeable increase in patients with more severe infection.
Your doctor may prescribe:
- Anticoagulants: These are medically referred to as blood thinners. These medications like heparin and warfarin prevent new clots from forming in your blood.
- Clot dissolvers (thrombolytics): These drugs break down a clot to improve blood flow and perfusion. They are reserved for people hospitalized in emergency situations because side effects may include dangerous bleeding problems.
- Minimally invasive methods or surgery might be essential on the off chance that you're temperamental due to the tricky clots and you really want dire reperfusion to further develop the bloodstream to your lungs and heart, particularly when thrombolytics cannot be utilized.
A few strategies a specialist might use on account of a pulmonary embolism include:
- Catheter-directed methods: These are utilized for cluster evacuation and breakdown. A dainty cylinder got down on a catheter will pull, separate, or break up clots in your pulmonary vein.
- Open surgery: Specialists utilize open surgery just in crisis circumstances when:
- Minimally invasive catheter-directed methods are not accessible.
- Prescriptions aren't attempting to separate the coagulation.
- Drugs are contraindicated or convey an excessive number of risks for the patient.
Outlook
A pulmonary embolism happens when a blood coagulation arrives at the lungs. These blood clots frequently come from deep vein thrombosis, which can result from harm to bone and muscle or from extensive stretches of inactivity. Commonly the specific reason for a DVT or pulmonary embolism is obscure in spite of a careful assessment.
A pulmonary embolism can be extremely risky, so it's essential to contact a clinical expert in the event that you're encountering symptoms, such as, chest pain, throwing up blood, and blacking out.
If you or anyone you know is suffering from the effects of Covid-19, our expert providers at Post Covid Centers will take care of your health and help you recover.
Call us on (469) 545-9983 to book a telehealth appointment for a home check-up.
People Also Read:
Post Covid Syndrome vs. Fatigue
While COVID-19 is a short-lived disease in most people, others experien...
Post Covid Syndrome vs. Skin Weakness Problems
A new study illustrates that some patients with COVID-19 disease have continuous skin-associated symptoms...
RELATED BLOGS
